Microbial production of cis,cis-muconic acid from hydrothermally converted lignocellulose
Seiten
2022
Cuvillier Verlag
978-3-7369-7589-7 (ISBN)
Cuvillier Verlag
978-3-7369-7589-7 (ISBN)
- Keine Verlagsinformationen verfügbar
- Artikel merken
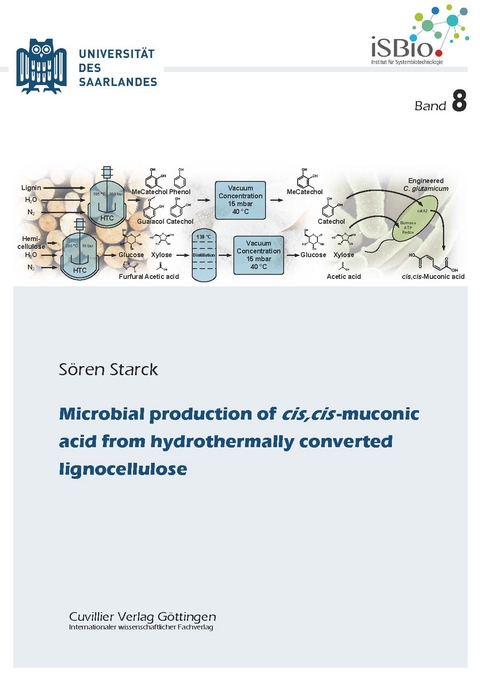
Cis,cis-muconic acid receives increasing interest to be produced from renewables. Catabolic microbial pathways can be tailored to accumulate cis,cis-muconic acid from a range of aromatic compounds. A renewable, sustainable and under-valued resource for aromatics is lignin. In this work, using hydrothermal conversion, lignin was depolymerized into hydrolysates with up to 615 mM aromatic monomer content. Catechol-rich hydrolysates were generated for bioconversion with the previously developed cis,cis-muconic acid producers P. putida MA-9 and C. glutamicum MA-2, whereas hydrolysates were guaiacol-rich for Amycolatopsis sp. MA-2. When grown with glucose as a co-substrate, C. glutamicum MA-2 yielded 2.6 g L⁻¹ (100 % yield) cis,cis-muconic acid from catechol. Towards an even more sustainable process, glucose was then replaced by hemicellulose, a non-food renewable. Hemicellulose, a co-constituent of lignin in lignocellulose, was hydrothermally converted into a mixture of C₅ and C₆ sugars. As hemicellulose was mainly converted into xylose (91 % yield), C. glutamicum MA-2 was engineered to utilize this pentose. Fed-batch bioconversion on a catechol-rich Kraft lignin hydrolysate as well as a hemicellulose hydrolysate using C. glutamicum MA-4 yielded 4 g L⁻¹ muconic acids. As the developed process was non-competitive to feed and food, it is a promising starting point for future application in bio-based industrial settings.
| Erscheinungsdatum | 19.03.2022 |
|---|---|
| Reihe/Serie | Hochschulschriften - Institut für Biotechnologie, Universität des Saarlandes ; 8 |
| Verlagsort | Göttingen |
| Sprache | englisch |
| Maße | 148 x 210 mm |
| Themenwelt | Medizin / Pharmazie ► Medizinische Fachgebiete ► Mikrobiologie / Infektologie / Reisemedizin |
| Naturwissenschaften ► Biologie | |
| Technik ► Maschinenbau | |
| Schlagworte | Activated charcoal • adipic acid • Amycolatopsis • Aromate • aromatics • bio-based ecomomy • bio-based industry • bio-basierte Industrie • bioconversion • Biokonversion • biomass • Bioraffinerien • Biorefineries • Catechol • Chemical Industry • Chemische Industrie • cis-Mukonsäure • Corynebacterium glutamicum • Depolymerisationsstrategie • Depolymerisierungsstrategie • depolymerization strategy • different wood species • Dioxygenase • Distillation • Fed-Batch • Fermentation • food crops • Fossile Ressourcen • fossil resources • Fraktionierungsmethoden • GC-MS • Guaiacol • Hemicellulose • HPLC • hydrothermal conversion • hydrothermale Umwandlung • Kraft process • Lignin • Lignintypen • Lignocellulose • Lignozellulosefraktionierung • lignozellulosehaltige Biomasse • low value side-stream • Metabolic Engineering • metabolisches Engineering • microbial factory • microbial pathways • mikrobielle Fabrik • mikrobielle Stoffwechselwege • Monomerausbeute • Muconic acid • muconic acid producers • Mukonsäureproduzenten • Nachwachsende Rohstoffe • Nahrungsindustrie • Nahrungspflanzen • Nebenproduktstrom • Non-Food-Materialien • non-food materials • Nylon • product accumulation • Produktanreicherung • Pseudomonas putida • renewable • renewable resources • Sustainable • Valorisierung • valorization • Vanillinmarkt • verschiedene Holzarten • xylose |
| ISBN-10 | 3-7369-7589-9 / 3736975899 |
| ISBN-13 | 978-3-7369-7589-7 / 9783736975897 |
| Zustand | Neuware |
| Haben Sie eine Frage zum Produkt? |
Mehr entdecken
aus dem Bereich
aus dem Bereich
und Erste Hilfe an Bord
Buch | Softcover (2024)
MWV Medizinisch Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft
CHF 55,90